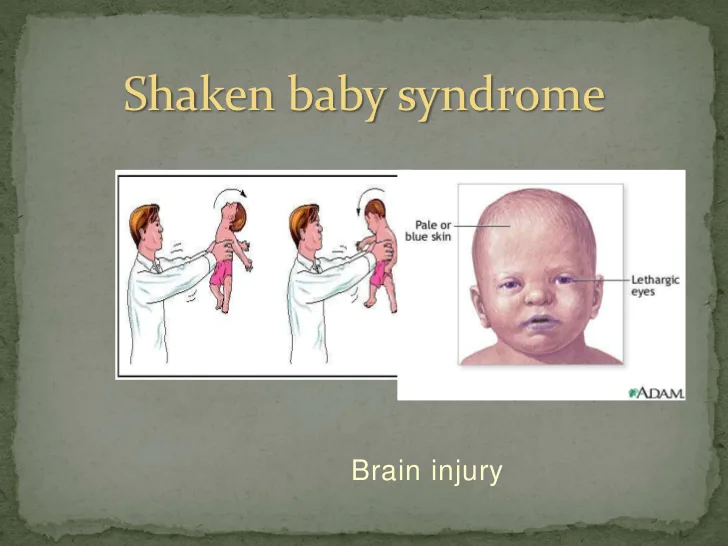
Shaken baby syndrome (SBS), sometimes known as abusive head trauma (AHT), is characterized by intracranial and retinal bleeding of an infant without an injury evidence and with normal coagulation profile. The main causes of the disorder include physical abuse, neglect, sexual harassment and emotional abuse. The newborns subjected to numerous types of abuses develop physical, emotional and cognitive conditions. In most instances, the magnitude of child abuse is underestimated due to their tender age, or the child abuse sequelae which makes the victims unable to articulate their problems.
A minimum of 40 cases of AHT occur annually in Canada, and research shows that 8 children die in the Canadian state, and 18 infants experiences neurological injury necessitating the need for life-long care and 17 are taken into foster care. The statistics shows that AHT is a disorder of economic importance and this raises an alarm to the concerned people to address it with immediate effect. SBS has serious effects on neurological functions and sometimes has multiple impacts on the neurocognitive functions.
The disease was first discovered by Guthkelch in 1971. The initial name used to describe SBS was ‘Whiplash-shaken infant syndrome.’ AHT is frequent in children of 2 years of age and below but the condition can also affect kids of up to 5 years of age. The paper will discuss SBS and its effects which cannot be underestimated because the disease leads to neurological injury and death in severe cases. Besides, the paper will also define and comment on Bevis tools; Caring, Teaching, and advocacy related to the information in the articles.
Prevention of Abusive Head Trauma
Abusive head trauma (AHT), also known as shaken baby syndrome (SBS), is a type of traumatic injury of the brain that was initially discovered by neurosurgeons in the early 1970s (Barr, 2012). The disease is characterized by intracranial and retinal bleeding of a newborn in absence of evidences of external injury and with normal coagulation profile. The violence resulting to such type of injuries is severe, dangerous and sometimes can lead to death of the child as pointed by a report released by American Academy of Pediatrics Committee of Child Abuse and Neglect. Unfortunately, AHT is a significant problem in Canada which records a minimum of 40 cases annually. The effects of AHT are extremely adverse with research pointing that 8 children out of these 40 cases meet their untimely death, 18 children suffer from neurological injury necessitating the need for lifelong care and 17 children end spending their lives in foster care settings.
SBS does not only cause cognitive damage, but also results in a lifelong financial challenges, with research pointing an average cost of $210, 012 per baby for less serious injuries and $1, 272, 900 for every fatal injury (Barr, 2012). According to research conducted by Barr (2012), the United States spends an approximated financial expense of $124 billion in the prevention, treatment and caring of the victims of AHT. The signs and symptoms of AHT include irritation, vomiting, fever, lethargy, apnea, tremors, excessive crying, and delays in development. The infants usually portray signs of injuries in the abdomen, long-bone and rib fractures, and patterned bruises.
There are several ways of preventing AHT according to research. The best method of reducing SBS is by educating the parents, teachers, healthcare specialists, and members of the community. The maternal-child nurses, emergency department specialists and other healthcare specialists are some of the important positions since they help in early recognition and execution of methods of prevention.
Implications for Practice
There are various tools applied by nurses in the output stage which helps the nurses in planning and providing care geared towards achieving a variety of client centered care goals. Some of these tools include caring, teaching and empowerment for self-responsibility & advocacy. The most suitable Bevis tool for the prevention of abusive head trauma article described above is the caring tool. Caring manifests itself in four stages namely; attachments, assiduity, intimacy, and confrontation. The caring tool creates a sense of self-awareness and other people, and transcends illness limits optimizing the actualization of potential in human beings. It is most appropriate in the research because training of healthcare professionals, parents, and members of the community portrays a high degree of caring who will in turn apply the knowledge gained in the care of victims of SBS.
A nationwide nurse training program for a hospital based infant abusive head trauma prevention program
AHT is the primary cause of traumatic death and injuries common in infants who are one year of age and below. There is a high probability of a newborn contracting AHT in the first year of life, usually 34 per 100, 000 infants. One of the activities which triggers shaking of a baby is inconsolable or excessive crying of the infants. The crying of the infants sometimes becomes a frustrating issue among the parents and other caregivers who fail to understand that crying is a normal stage in the development of a child and declines as the baby grows old.
Currently, the common AHT prevention method is the hospital-based universal AHT prevention program. The programs are usually delivered to parents during the postpartum period. Evidence shows that 23 states of the U.S have implemented a legislation which makes it mandatory for concerned healthcare specialists to offer education to all new parents about SBS and the risks associated with the shaking of the baby. Majority of the programs provides all the new parents with the knowledge concerning normal crying of the infants and the dangers of shaking although their content, methods of delivery and quality of the information offered varies. According to research, the cases of SBS have decreased due to the implementation of hospital-based education programs for the new parents.
Implications for Practice
The most suitable Bevis tool for application in the above article of hospital-based education programs is the teaching tool. Teaching is an activity developed in the facilitation of the learning process. It is a process of creating a setting where learning can take place and this has been done in 23 states of the United States. All the new parents are taught on the normal crying of the infants and potential risks associated with baby shaking. The teaching and learning becomes shared and reciprocal between the nurse, health-team and the client.
The Role of a Nurse Practitioner in Diagnosing Child Abuse
It is important for a nurse specialist to be familiar with the deficiencies which negatively impact the health of children, adults and adults. All types of child abuse have detrimental effects, and thus healthcare provider should be aware some of the abuses exist alone whereas others exist in combination when performing patient evaluations. Therefore, making accurate diagnosis is vital since some infants exhibit a vast range of symptoms after abuse. Some of the symptoms of child abuse include vomiting, abdominal distention, irritation, anemia, lethargy and shock. Other signs of sexual abuse include sleep disorders, phobias and changes in behavior. Sometimes a healthcare practitioner may establish a vague complaint such as sleep disturbance, or sexually transmitted disease in the diagnosis of a victim of child abuse.
Implications for Practice
The most suitable Bevis tool for linking the role of a nurse practioner in diagnosing child abuse is empowerment for self-responsibility and advocacy. In this case, nurses work hard in the healthcare settings by proper direction of resources, personnel, processes and tools at their disposal to attain optimal health, and well-being. The whole process of empowerment for self-responsibility and advocacy is portrayed in the nurses who are always committed in their roles of diagnosing child abuse cases. Empowerment and self-responsibility succeeds in cases where there is hope and optimism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of SBS came up with various findings. Some of the negative impacts of AHT are cognitive damages to the infant and financial strain to the parents. Education of parents, healthcare practitioners, teachers and members of the community is the best method of minimizing the cases of AHT. Hospital-based AHT intervention programs provides knowledge to new parents about the normal infant crying and the dangers associated with baby shaking. The programs have proved effective in reducing the cases of SBS. The nurse specialist needs to be careful to make an accurate diagnosis because some infants show a varied range of symptoms after the child abuse.