Managing industrial wastewater is a critical challenge in today’s rapidly growing industries. Sectors such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing produce large volumes of wastewater containing chemicals, oils, heavy metals, and suspended solids. Untreated, this wastewater can pollute rivers, lakes, and groundwater, threaten aquatic life, and disrupt ecosystems.
An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) provides a reliable solution for treating industrial wastewater effectively. It ensures compliance with environmental regulations, reduces water consumption, and supports sustainable practices.
MKS Industrial Solutions, as a leading provider of industrial wastewater management systems, delivers advanced and customized ETP solutions. Their systems are designed to handle various wastewater types efficiently, enabling industries to implement safe, eco-friendly, and cost-effective water management strategies.
What is an Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)?
An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) is a facility that treats industrial wastewater, removing harmful contaminants before the water is discharged into the environment or reused within the plant. Industrial wastewater can contain organic and inorganic compounds, oils, heavy metals, and suspended solids, making it dangerous if released untreated.
Depending on the industrial process, ETPs can effectively treat various types of wastewater, including:
Chemical-laden water: Contains acids, alkalis, and solvents from chemical and manufacturing processes.
Oily wastewater: Found in refineries, chemical plants, and food processing industries.
Suspended solids and organic matter: Includes dirt, biodegradable waste, and process residues.
Using an ETP reduces environmental risks, promotes water recycling, and conserves freshwater resources.
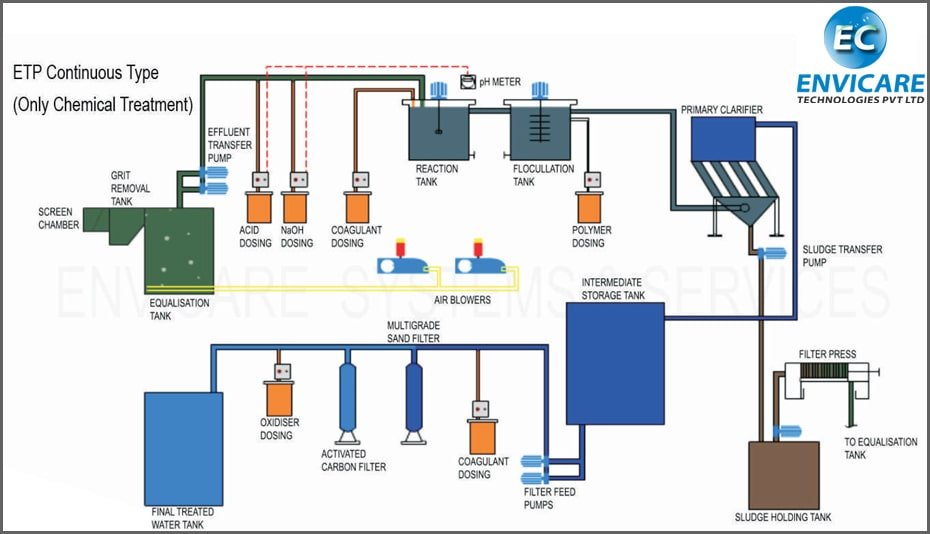
How Does an Effluent Treatment Plant Work?
ETPs typically operate in five main stages, each designed to remove specific contaminants and ensure high-quality treated water.
1. Preliminary Treatment
Purpose: Remove large debris and solids.
Screens, bar racks, and grit chambers filter out stones, plastics, sand, and other debris.
Protects pumps, pipelines, and downstream equipment from damage.
Prevents clogging and ensures smooth operation in later stages.
2. Primary Treatment
Purpose: Remove suspended solids and floating oils.
Sedimentation tanks or clarifiers allow heavy particles to settle as sludge.
Lighter substances like oil and grease float to the surface and are skimmed off.
Reduces pollutant load for secondary biological treatment.
3. Secondary Treatment
Purpose: Remove dissolved and biodegradable organic matter using microorganisms.
Aerobic treatment: Microorganisms use oxygen to break down organic matter efficiently.
Anaerobic treatment: Microorganisms work without oxygen to degrade complex compounds; suitable for high-strength wastewater and can produce biogas.
This stage significantly improves water quality and prepares it for tertiary treatment.
4. Tertiary Treatment
Purpose: Achieve high-quality, safe effluent.
Filtration: Removes fine suspended particles.
Chemical treatment: Neutralizes toxic compounds and adjusts pH.
Disinfection: Chlorination or UV treatment eliminates harmful pathogens.
Tertiary treatment is crucial for industries practicing water reuse or aiming for Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD).
5. Sludge Management
Purpose: Handle sludge safely and sustainably.
Sludge from primary and secondary stages is dewatered.
Proper handling prevents environmental contamination.
Some industries convert sludge into energy or compost, enhancing sustainability.
Key Benefits of Using an ETP
Implementing an ETP offers multiple advantages:
Environmental Protection: Reduces pollution in rivers, lakes, and groundwater, safeguarding ecosystems and public health.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensures industries meet standards set by authorities like CPCB and SPCB, avoiding fines.
Water Reuse & Cost Savings: Treated water can be reused in industrial processes, cooling systems, or irrigation.
Enhanced Reputation: Demonstrates a company’s commitment to sustainability and responsible operations.
Customizable Solutions: ETPs can be designed to meet specific industry requirements, wastewater types, and capacities.
Investing in an ETP is more than regulatory compliance—it is a strategic step toward sustainable growth and operational efficiency.
Industries That Use ETPs
ETPs are widely adopted across multiple sectors:
Textile & Dyeing: Treats chemically and color-laden wastewater.
Pharmaceuticals: Removes toxic chemicals and organic residues.
Chemical & Petrochemical: Handles hazardous and highly polluting wastewater streams.
Food & Beverage: Treats wastewater rich in organic matter and process effluents.
Tanneries: Removes heavy metals, dyes, and suspended solids.
The versatility of ETP systems allows them to adapt to different wastewater types and plant sizes, making them essential for modern industries.
Emerging Trends in ETP Technology
Modern ETPs are evolving to improve efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and minimize environmental impact. Key trends include:
Automation & IoT Integration: Real-time monitoring of water quality and flow ensures faster corrective actions.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): Complete water recycling with no wastewater discharge.
Energy-Efficient Processes: Low-energy treatment methods reduce operational costs and carbon footprint.
Advanced Membrane Filtration: Improves removal of dissolved solids and micropollutants for high-quality effluent.
These advancements make ETPs more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient.
Conclusion
An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) is essential for industries seeking sustainability, regulatory compliance, and efficient operations. Properly treated wastewater helps industries:
Protect rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Comply with environmental regulations.
Reduce freshwater consumption and operational costs.
Enhance their reputation as responsible businesses.
Advanced ETP systems ensure compliance, conserve water, protect the environment, and support long-term sustainable development. To learn more about how a customized ETP system can benefit your business, contact the experts at MKS Industrial Solutions today.